Nov 18, 1998 · Subsequently, the term relative risk commonly refers to either the risk ratio or the odds ratio However, only under certain conditions does the odds ratio approximate the risk ratio Figure 1 shows that when the incidence of an outcome of interest in the study population is low (Dec 30, 16 · INTRODUCTION Odds ratio (OR) and risk ratio (RR) are two commonly used measures of association reported in research studies In crosssectional studies, the odds ratio is also referred to as the prevalence odds ratio (POR) when prevalent cases are included, and, instead of the RR, the prevalence ratio (PR) is calculatedOct 27, 17 · However, one can calculate a risk difference (RD), a risk ratio (RR), or an odds ratio (OR) in cohort studies and randomized clinical trials Consider again the data in the table below from the randomized trial assessing the effectiveness of a newly developed pain reliever as compared to the standard of care

Society For Birth Defects Research And Prevention
Odds ratio vs relative risk cohort
Odds ratio vs relative risk cohort-May 14, 21 · The odds ratio (OR) or the ratio of odds of exposure is thus given by a/cb/d (or ad/bc) The odds ratio is generally a good estimate of the relative risk The terms odds ratio and relative risk are in fact interchangeable when used in casecontrol studies Population and hospitalbased casecontrols studiesMay 18, 12 · Examples of measures of association include risk ratio (relative risk), rate ratio, odds ratio, and proportionate mortality ratio Risk ratio Definition of risk ratio A risk ratio (RR), also called relative risk, compares the risk of a health event (disease, injury, risk factor, or death) among one group with the risk among another group



Relative Risk Wikipedia
9222 Measures of relative effect the risk ratio and odds ratio Measures of relative effect express the outcome in one group relative to that in the other The risk ratio (or relative risk) is the ratio of the risk of an event in the two groups, whereas the odds ratio is the ratio of the odds of an event (see Box 92a)For both measures a value of 1 indicates that the estimated effectsApr 06, 10 · Here's the key Relative Risk looks to the future for the effect of a particular cause hence it is used in prospective studies say a cohort study Lets compare the above with Odds Ratio The Odds Ratio can be addressed by asking te following question How many times more likely is a diseased group to have been exposed to a risk factor asOct 27, 11 · Davies et al (1) state that the odds ratio is a common measure in casecontrol studies, cohort studies, or clinical trails Unfortunately, this first sentence of their article is not correct For different study designs, OR should only be used as a measure of effect size when RR can not be estimated directly
Jan 10, 13 · Odds ratio vs relative risk Odds ratios and relative risks are interpreted in much the same way and if and are much less than and then the odds ratio will be almost the same as the relative risk In some sense the relative risk is a more intuitive measure of effect sizeFeb 24, 13 · 5 Odds ratio can be calculated in a cohort study and in a casecontrol study The exposure odds ratio is equal to the disease odds ratio Relative risk can only be calculated in a cohort study Odds ratio can be a measure of relative risk in case control study 6Apr , · We illustrated both relative risks and odds ratios using bar charts, then looked at the types of study for which each statistic is suited We demonstrated calculation of relative risks and odds ratios through analysis of tabled data from a recent published longitudinal study, using a 2 × 2 table and R, the open‐source statistical programming
Oct 01, 07 · The 95% CI is the interval that includes the 95% of risk ratios of these 100 population samples Thus, the 95% CI is the interval of values in which the true risk ratio is likely to lie with a probability of 95% To be statistically significant with a PIn epidemiological terms, the odds ratio is used as a point estimate of the relative risk in retrospective studies I understand that odds ratio is calculated in case control studies, while relative risk is calculated in cohort studiesMay 04, 09 · When the outcome risk is 01 or less, odds ratios and risk ratios agree well for risk ratio values ranging from 01 to 10 in all 3 figures When cumulative incidence is 10, the odds ratio is within 10% of the risk ratio for risk ratios ranging from 01 to 18 in Figure 1, from 055 to 10 in Figure 2, and from 04 to 25 in Figure 3 When


Marg Innovera



Figure 2 From Secondhand Smoke Exposure And Risk Of Lung Cancer In Japan A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis Of Epidemiologic Studies Semantic Scholar
May 15, 12 · The risk ratio, also referred to as the relative risk, is calculated as the ratio of the risk of the outcome in these two groups In this article, we illustrate, by means of two empirical examples, that use of odds ratios in cohort studies andApr 14, 17 · Other O does not have an R (cOhort), which means the other group does not have the risk factor Compare the two to see who gets the disease How to remember that case control studies measure odds ratio and cohort studies measure relative risk You take surgical "cases" to the "OR" (Operating room) Case control study Odds Ratio cohoRRRRRRtRisk Ratio 31 • Can also be called Relative Risk or RR Exposure odds ratio • Similar to risk ratio from cohort study • PR= Prevalence of disease in exposed group/ Prevalence of disease in unexposed group OR



Analytical Studies Note Cohort Study Gives Incidence Relative Risk A R P A R Natural History Of Disease Cohort Study Case Control Study Study



Relative Risks And Odds Ratios What S The Difference Mdedge Family Medicine
Aug 01, 03 · In a matched cohort study of crash data, the risk ratio of death for those who wore a seat belt compared with those unbelted was estimated as 039 (95 percent confidence interval 037, 041) using conditional Poisson regression;When used for cohort studies and randomized clinical trials, the odds ratio is often incorrectly interpreted as the risk ratio;Statistical use and meaning Relative risk is used in the statistical analysis of the data of ecological, cohort, medical and intervention studies, to estimate the strength of the association between exposures (treatments or risk factors) and outcomes Mathematically, it is the expressed as the incidence rate of the outcome in the exposed group, , divided by the outcome of the unexposed



The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor


Odds Ratios Need To Be Graphed On Log Scales Andrew Wheeler
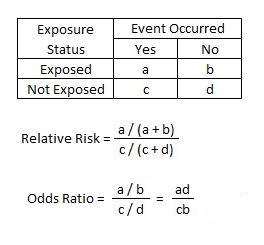
Odds ratio = odds of exposure (cases) = ad odds of exposure (controls) bc Cohort studies The relative risk is the measure of association for a cohort study It tells us how much more likely (or less likely) it is for people exposed to a factor to develop a disease compared to peopleAug 26, · Risk ratios, odds ratios, and hazard ratios are three ubiquitous statistical measures in clinical research, yet are often misused or misunderstood in their interpretation of a study's results A 01 paper looking at the use of odds ratios in obstetrics and gynecology research reported 26% of studies (N = 151) misinterpreted odds ratios as risk ratios , while aAs an extreme example of the difference between risk ratio and odds ratio, if action A carries a risk of a negative outcome of 999% while action B has a risk of 990% the relative risk is approximately 1 while the odds ratio between A and B is 10 (1% =



When Can Odds Ratios Mislead The Bmj


Case Control And Cohort Studies A Brief Overview Students 4 Best Evidence
Jul 11, 16 · If the relative risk is 1, the tutoring made no difference at all If it's above 1, then the tutored group actually had a higher risk of failing than the controls Odds Ratio The odds ratio is the ratio of the odds of an event in the Treatment group to the oddsNonexposed group, "OR" is an odds ratio from a logistic regression equation, and "RR" is an estimated relative risk Most researchers apply this formula to the adjusted odds ratio to estimate an adjusted relative risk Using the formula in this manner is incorrect and will produce a biased estimate when confounding is presentRisk ratios When risks are computed in a study, the risk ratio is the measure that compares the Risk exposed to the Risk unexposed The risk ratio is defined as the risk in the exposed cohort (the index group) divided by the risk in the unexposed cohort (the reference group) A risk ratio may vary from zero to infinity Risk Ratio = a / (ab


Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1


Research Statistics Basics Contents 1 Basic Concepts 2 References Basic Concepts Null Hypothesis The Hypothesis That The Independent Variable Has No Effect On The Dependent Variable For Example Steroids Do Not Improve Outcomes In Ards Would Be
Converting Odds Ratio to Relative Risk in Cohort Studies with Partial Data Information Zhu Wang Connecticut Children's Medical Center Abstract In medical and epidemiological studies, the odds ratio is a commonly applied measure to approximate the relative risk or risk ratio in cohort studies It is well known tha suchMay 15, 14 · The difference between odds ratio and risk ratio May 15, 14 • ericminikel The other day I was emailing with a statistical genetics colleague about a rare SNP associated with a phenotype I stated that the minor allele frequency (MAF) was 07% in cases and 01% in controls, for a risk ratio of 7 After clicking send, I felt a twinge of regretHi, Been reading through a research paper that used a prospective cohort study, but in the results table for measures of association, the odds ratio was used instead of relative risk


Matched Pair Case Control Statcalc User Guide Support Epi Info Cdc



Odds Ratio Wikipedia
Oct 03, 11 · Given that this is a cohort study, the relative risk (RR) should have been calculated instead of the odds ratio Odds ratios frequently generate larger differences between exposed and nonexposed groups (especially when dealing with nonrare events), therefore overestimating the observed effect (4)The odds ratio can also be used to determine whether a particular exposure is a risk factor for a particular outcome, and to compare the magnitude of various risk factors for that outcome OR=1 Exposure does not affect odds of outcome OR>1 Exposure associated with higher odds of outcome OR"OR" stands for "odds ratio" and "RR" stands for "relative risk" A retrospective cohort study, also called a historic cohort study, is a longitudinal cohort



Measures Of Association Ppt Download



Relative Risk Wikipedia
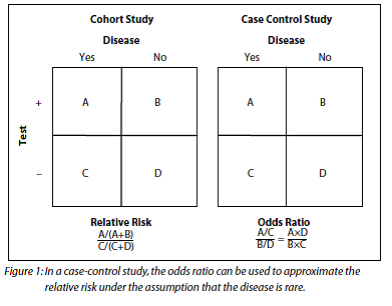
Feb 01, 18 · 2) Cohort studies will have information about persontime at risk, and so the desired outcomes are often incidence rates, population attributable risk, or risk ratios The odds ratio estimate for rare outcomes will approximately estimate the risk ratio in this design, but it makes more sense to compute the risk ratio directlyRR and OR are commonly used measures of association in observational studies In this video I will discuss how to interpret them and how to apply them to patPercent, population attributable risk percent, relative risk, odds, odds ratio, and others The concept and method of calculation are explained for each of these in simple terms and with the help of examples The interpretation of each is presented in plain English rather than in technical language Clinically useful notes are provided,



Phs 2101 Lecture Notes Summer 19 Lecture 4 Relative Risk Cohort Study Odds Ratio


Case Control Study Odds Ratio Relative Risk Best Custom Academic Essay Writing Help Writing Services Uk Online Homeworknowcomlink Web Fc2 Com
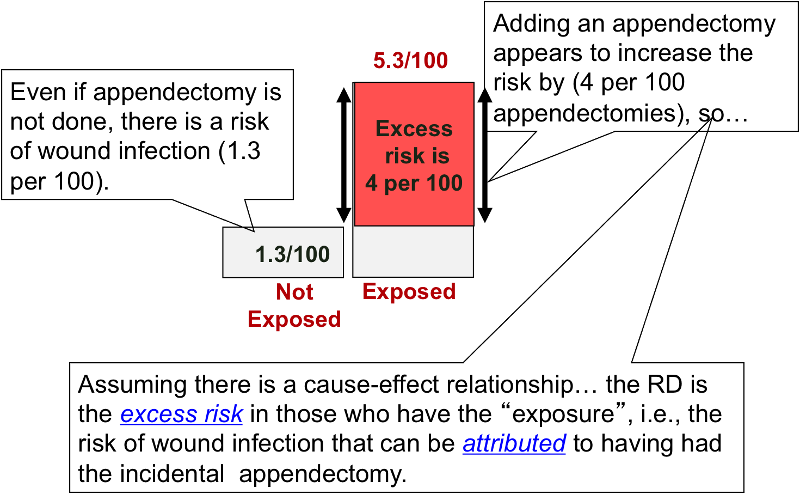
The odds ratio then provides an overestimation of the risk ratio, especially when the outcome is frequent The use of logistic regression to adjust for confounding is one of the reasons that odds ratios are presentedOdds ratios (OR) are commonly reported in the medical literature as the measure of association between exposure and outcome However, it is relative risk that people more intuitively understand as a measure of association Relative risk can be directly determined in a cohort study by calculating a risk ratio (RR)The odds ratio of death was 028 using conditional logistic regression (18, 61)


Using R For Biomedical Statistics Biomedical Statistics 0 2 Documentation
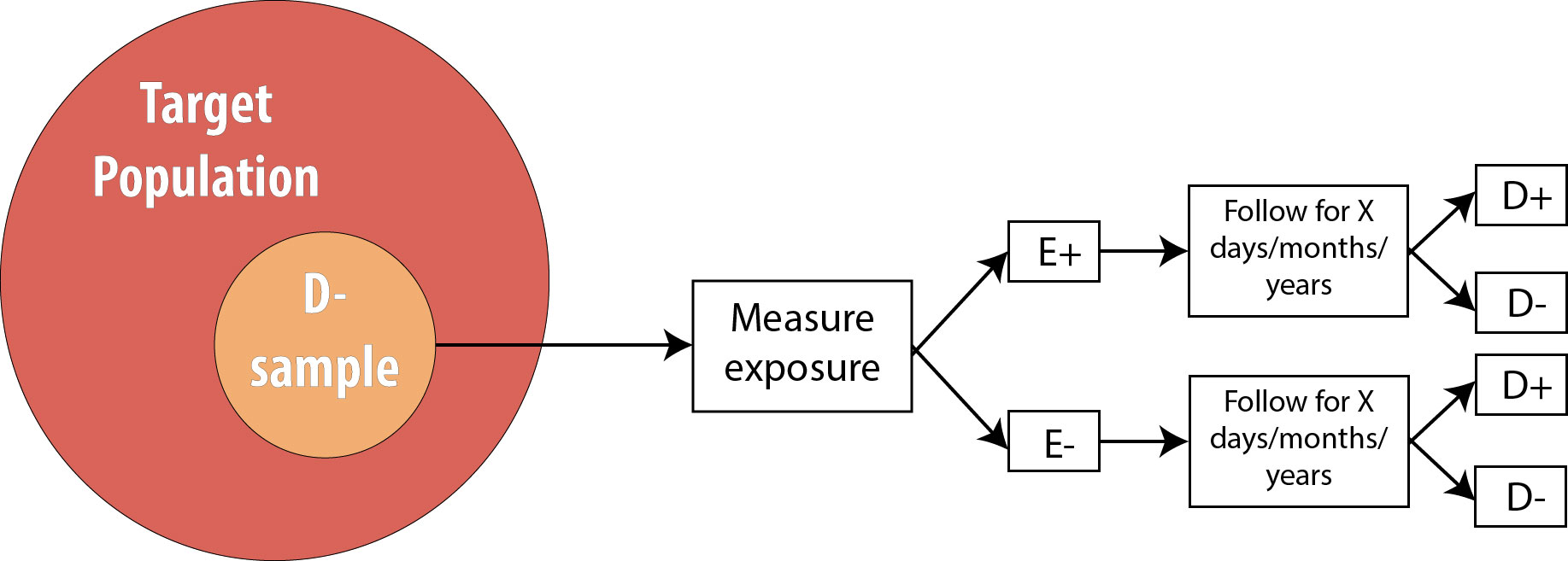


Introduction To 2 X 2 Tables Epidemiologic Study Design And Measures Of Association Foundations Of Epidemiology
Relative Risk (RR) is a ratio of probabilities or put another way it is one probability divided by another Odds Ratio (OR) is a ratio or proportion of odds I just remember that odds ratio is a ratio of odds and probability isn't a ratio of odds (AKA it is the other option) Relative Risk = Probability / ProbabilityERRATA At about the 300 mark the slide says "10,00" when it is really supposed to say "10,000" I added a pop up box to fix it Thanks to Mehdi Hedjazi forThe Odds Ratio The odds of disease in the exposed group are 7/10, and the odds of disease in the nonexposed group are 6/56 If I compute the odds ratio, I get (7/10) / (5/56) = 656, very close to the risk ratio that I computed from data for the entire population We will consider odds ratios and casecontrol studies in much greater depth in



Measures Of Association Stats Medbullets Step 1



1 Relative Risks Odds Ratios Or Hazard Ratios Of Risk Factors For Download Table
The relative risk is best estimated using a population sample, but if the rare disease assumption holds, the odds ratio is a good approximation to the relative risk — the odds is p / (1 − p), so when p moves towards zero, 1 − p moves towards 1, meaning that the odds approaches the risk, and the odds ratio approaches the relative riskOdds ratio can be calculated in a cohort study and in a casecontrol study − The exposure odds ratio is equal to the disease odds ratio Relative risk can only be calculated in a cohort study 33 When Is Odds Ratio a Good Estimate of Relative Risk?Mar 28, 1998 · The difference between the odds ratio and the relative risk depends on the risks (or odds) in both groups So for any reported odds ratio, the discrepancy between that odds ratio and the relative risk depends on both the initial risk and the odds ratio itself



Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios



Calculation Of Relative Risks Rr And Odd Ratios Or Download Table
In epidemiological terms, the odds ratio is used as a point estimate of the relative risk in retrospective studies Odds ratio is the key statistic for most casecontrol studies In prospective studies, Attributable riskor risk difference is used to quantify risk in the exposed group that is attributable to the exposureJul 01, 17 · This format is commonly expressed in cohort studies using logistic regression When the incidence of an outcome is low (



Retrospective Cohort Study Wikipedia



Estimating Risk



Math3010 Week 6



Using Odds Ratio In Case Control Studies Youtube



How To Interpret And Use A Relative Risk And An Odds Ratio Youtube
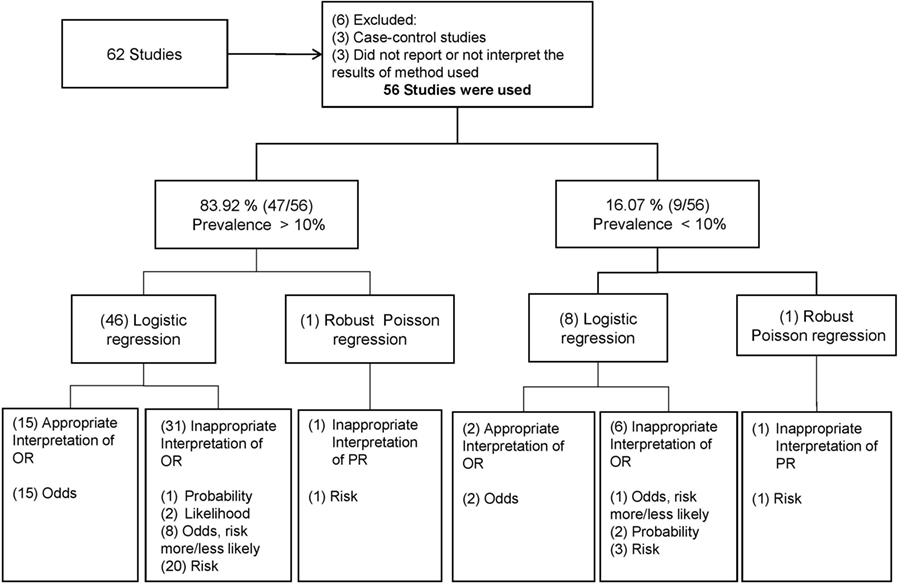


Frontiers Odds Ratio Or Prevalence Ratio An Overview Of Reported Statistical Methods And Appropriateness Of Interpretations In Cross Sectional Studies With Dichotomous Outcomes In Veterinary Medicine Veterinary Science



Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals



Frontiers Odds Ratio Or Prevalence Ratio An Overview Of Reported Statistical Methods And Appropriateness Of Interpretations In Cross Sectional Studies With Dichotomous Outcomes In Veterinary Medicine Veterinary Science



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1


What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora



Chapter 6 Choosing Effect Measures And Computing Estimates Of Effect Cochrane Training
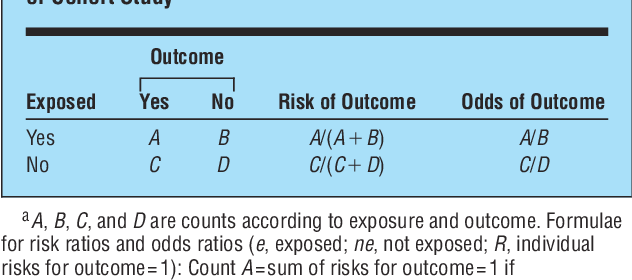


Table 1 From The Relative Merits Of Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios Semantic Scholar



Average Values Measures Of Association N Absolute Risk The Relative Risk And Odds Ratio Provide A Measure Of Risk Compared With A Standard N Attributable Ppt Download



What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean



A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence



Study Design Comparison Cohort Study Relative Risk



Risks Of And Risk Factors For Covid 19 Disease In People With Diabetes A Cohort Study Of The Total Population Of Scotland The Lancet Diabetes Endocrinology



Math3010 Week 6



Research Techniques Made Simple Interpreting Measures Of Association In Clinical Research Sciencedirect



Converting An Odds Ratio To A Range Of Plausible Relative Risks For Better Communication Of Research Findings The Bmj



Relative Risk Or Odds Ratio For Cardiovascular Disease Incidence Download Scientific Diagram



Believability Of Relative Risks And Odds Ratios In Abstracts Cross Sectional Study The Bmj


Case Control Studies



Relative Risk Wikipedia



Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Kidney International



Society For Birth Defects Research And Prevention



Moving Beyond Odds Ratios Estimating And Presenting Absolute



Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Sciencedirect


Relative Risk Article


How To Be Awesome At Biostatistics And Literature Evaluation Part Ii Tl Dr Pharmacy



Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1



A Most Odd Ratio Interpreting And Describing Odds Ratios Abstract Europe Pmc



Forest Plot Of Relative Risks And Odds Ratios Of Lung Cancer Associated Download Scientific Diagram


Case Control Study Vs Cohort Study Pp Made Easy In Population Perspective Made Easy On Vimeo



Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube


Risk Differences And Rate Differences


Case Control Study Vs Cohort Study Pp Made Easy In Population Perspective Made Easy On Vimeo



Relative And Atribute Risk



Cohort Case Control Studies Http Www Slideshare Net Terryshaneyfelt7 What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative R Cohort Study Academic Research Research Methods



Relative Risk And Absolute Risk Definition And Examples Statistics How To


Plos One Bleeding Risk With Long Term Low Dose Aspirin A Systematic Review Of Observational Studies



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1


Main Points To Be Covered Measures Of Association In Case Control Studies Prevalent Controls Design Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk And The Rare Disease Ppt Download


Event Based Measures Of Effect Size Asha Journals Academy


Case Control Studies Statistical Analysis Ppt Video Online Download



Relative Risk And Odds Ratio Usmle The Journey



Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk



Questionable Utility Of The Relative Risk In Clinical Research A Call For Change To Practice Journal Of Clinical Epidemiology



Beabletocalculate Direct Age Adjustment Proport Chegg Com



A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence



Learning And Applying Biostatistics How The Guinness Brewery


3 5 Bias Confounding And Effect Modification Stat 507


Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals



Relative Risk Versus Odds Ratio Usmle Biostatistics 4 Youtube



Numerators Denominators And Populations At Risk Health Knowledge
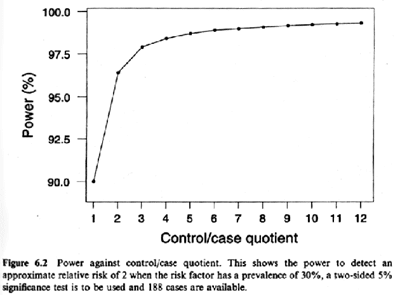


Lesson 9 Cohort Study Design Sample Size And Power Considerations For Epidemiologic Studies



What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora


Content



Odds Ratio Relative Risk Risk Difference Statistics Tutorial 30 Marinstatslectures Youtube



Ppt The Odds Ratio Relative Odds Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 6056
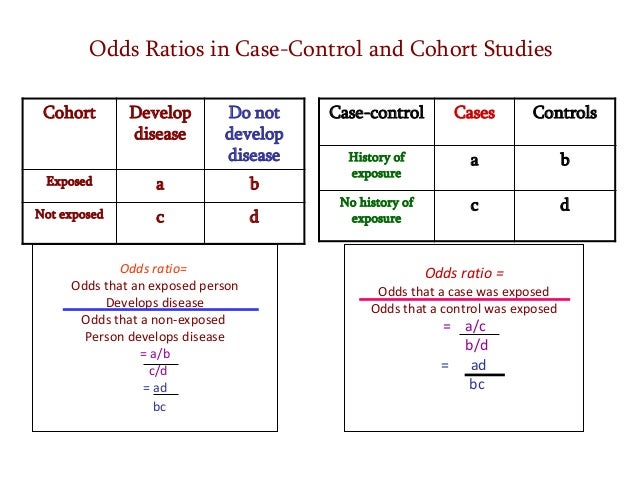


Estimating Risk



Questionable Utility Of The Relative Risk In Clinical Research A Call For Change To Practice Journal Of Clinical Epidemiology


9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 Review Odds Ratios Are Calculated From Case Control Studies Which Are Described On Slide 14 Odds Ratios Are Only Estimates Of Relative Risks Since True Incidence Rates Cannot Be



Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios



Questionable Utility Of The Relative Risk In Clinical Research A Call For Change To Practice Journal Of Clinical Epidemiology



A Practical Overview Of Case Control Studies In Clinical Practice Chest



Research Techniques Made Simple Interpreting Measures Of Association In Clinical Research Sciencedirect



Comparison Of Three Methods For Estimating Relative Risk In A Cohort Download Table


Icare An R Package To Build Validate And Apply Absolute Risk Models



Measures Of Association Ppt Download
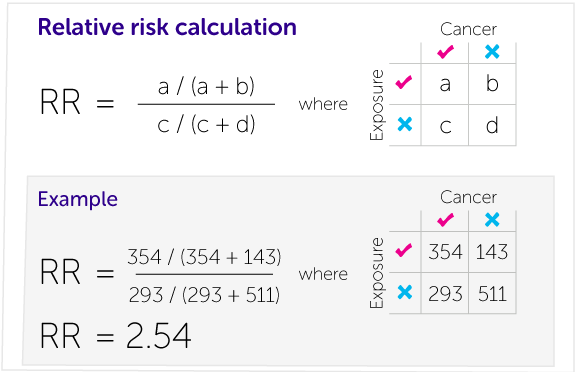


Our Calculations Explained Cancer Research Uk



Reporting The Results Sage Research Methods



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿