In the expression, if we replace y with (− y), we will get the identity x 3 − y 3This algebraic identity can be written in the following form too ( a − b) 3 = a 3 − b 3 − 3 a 2 b 3 a b 2 Generally, the a minus b whole cubed algebraic identity is called by the following three ways in mathematics The cube of difference between two terms identity or simply the cube of difference identity The cube of a binomial formula #(xy)^3=(xy)(xy)(xy)# Expand the first two brackets #(xy)(xy)=x^2xyxyy^2# #rArr x^2y^22xy# Multiply the result by the last two brackets #(x^2y^22xy)(xy)=x^3x^2yxy^2y^32x^2y2xy^2# #rArr x^3y^33x^2y3xy^2#

Pdf On Trace Forms On A Class Of Commutative Algebras Satisfying An Identity Of Degree Four
(x y)^3 identity
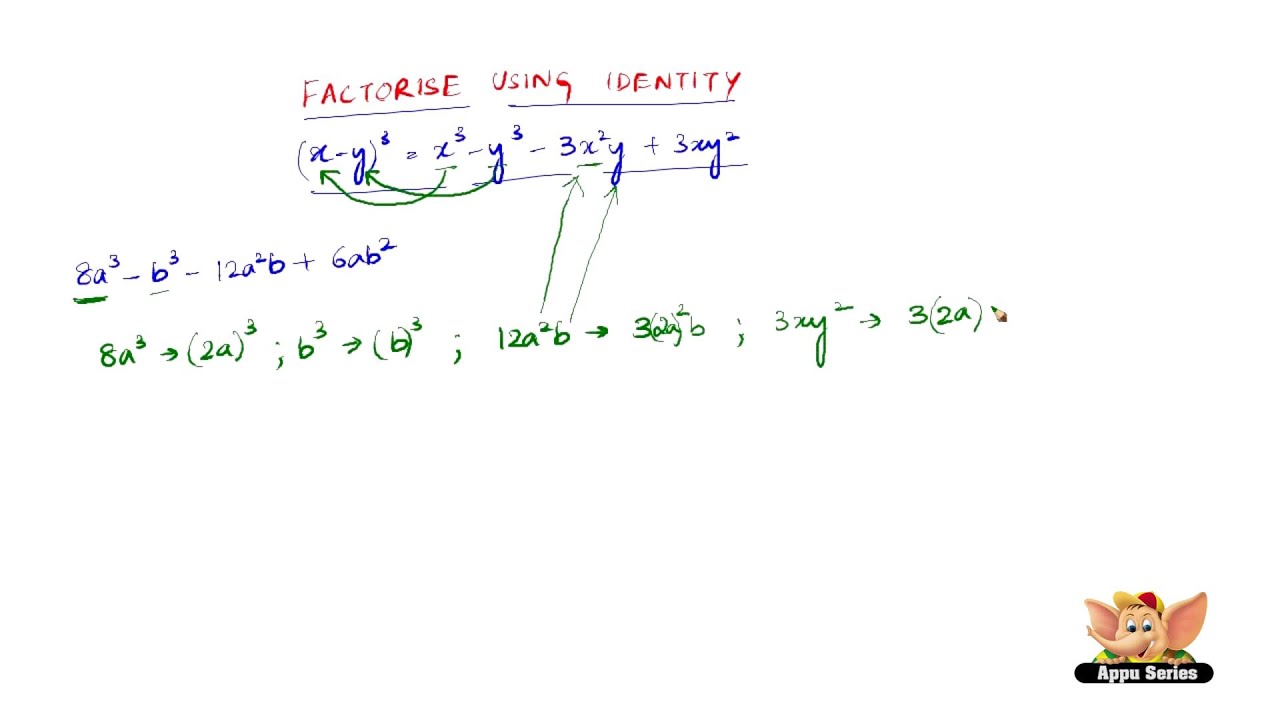
(x y)^3 identity- Identity (x – y) 3 = x 3 – y 3 – 3xy(x – y) (1000 – 2) 3 = 1000 3 – 2 3 – 3*1000*2(1000 – 2) = – 8 – 6000(1000 – 2) = – 8 – 100 = Factorise each of the following (i) 8a 3 b 3 12a 2 b 6ab 2 (ii) 8a 3 – b 3 – 12a 2 b 6ab 2 (iii) 27 – 125a 3 – 135a 225a 2Python Identity Operators Identity operators are used to compare the objects, not if they are equal, but if they are actually the same object, with the same memory location Operator Description Example Try it is Returns True if both variables are the same object x is y




Given A X 3 Y 3 If A 3i Where I Is The Identity Matrix Of Order 2 Find X And Y Brainly In
We can use the Cosine Sum Identity to combine the terms on the left into a single term, and we can solve the equation from there Now when or for integers Thus, \ (\cos (\theta \dfrac {\pi} {5}) = \dfrac {\sqrt {3}} {2} \) when or Solving for 313 Suppose that you are given a system of two equations of the following form Acos ϕ = Bν1 − Bν2 cos θ Asin ϕ = Bν2sin θ Show that = B2(ν2 1 ν2 2 − 2ν1ν2 cosθ ) For Exercises 416, prove the given identity 314 cos θ tan θ = sinθ 315 sinθ cot θ = cos θ 316 tan θ cot θ = tan2 θ Answer (d) Now, (x y)3 – (x3 y3) = (x y) – (x y)(x2– xy y2) using identity, a3 b3 = (a b)(a2 ab b2) = (x y)(x y)2 (x2 xy y2)
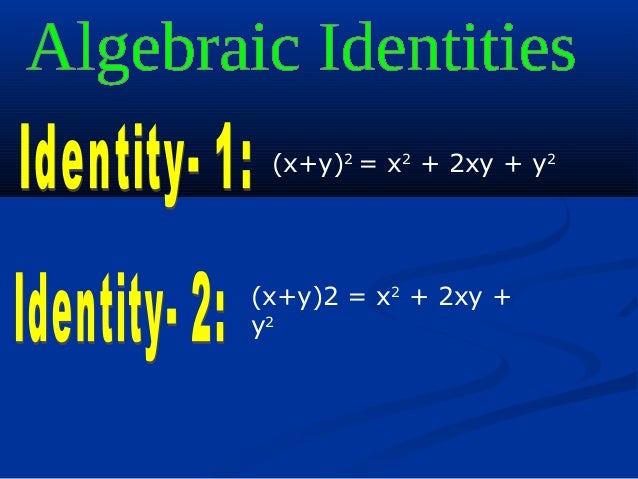
It is read as $x$ plus $y$ whole cube It is mainly used in mathematics as a formula for expanding cube of sum of any two terms in their terms ${(xy)}^3$ $\,=\,$ $x^3y^33x^2y3xy^2$ Proofs The cube of $x$ plus $y$ identity can be proved in two different mathematical approaches Algebraic method Learn how to derive the expansion of cube of $x$ plus $y$ identity by theTrigonometric Identities Solver \square!1) associative 2) additive identity 3) additive inverse 4) distributive 3 Tori computes the value of 8⋅95 in her head by thinking 8(100−5) =8×100−8×5 Which
Seeking a contradiction, we assume that there are matrices X and Y such that XY − YX = I Then we take the trace of both sides and obtain n = tr(I) = tr(XY − YX) = tr(XY) − tr(YX) (by property (1), (2) of the trace) = tr(XY) − tr(YX) (by property (3) of the trace) = 0 Since n is a positive integer, this is a contradictionReplacing y with (−y) in the identity, (xy)3=x33x2y3xy2y3∗) (valid for any elements x , y of a commutative ring), which explains the name "binomial coefficient" Another occurrence of this number is in combinatorics, where it gives the number of ways, disregarding order, that k objects can be chosen from among n objects;




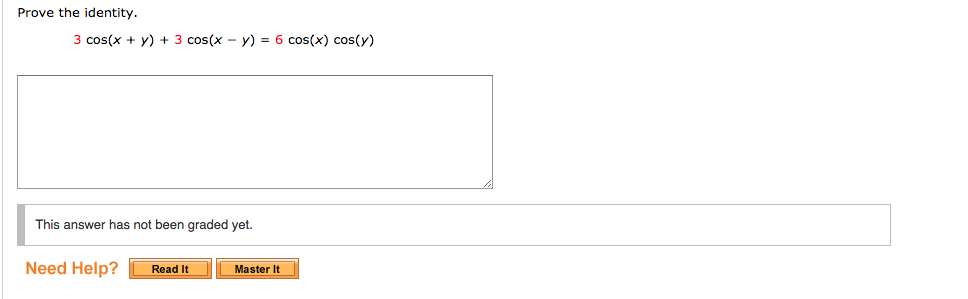
Prove The Identity 3 Cos X Y 3 Cos X Y 6 Cos X Chegg Com




Algebraic Expressions And Identities Class 8 Maths Geeksforgeeks
Identity that i2 = 1, meaning that iis a square root of 1 If z= xiy2C, we call x=Factor x^3y^3 x3 − y3 x 3 y 3 Since both terms are perfect cubes, factor using the difference of cubes formula, a3 −b3 = (a−b)(a2 abb2) a 3 b 3 = ( a b) ( a 2 a b b 2) where a = x a = x and b = y b = y (x−y)(x2 xyy2) ( x y) ( x 2 x y y 2)The coefficient of the \ (x^ {3k}y^k\) term is counting the number of terms that have \ (y^k\) \ ( (xy)^3 = \binom30 x^3y^0 \binom31 x^2y^1 \binom32 x^1y^2 \binom33 x^0y^3\) 🔗 Theorem 532 The Binomial Theorem Let x and y x and y be variables and n n a natural number, then




Rd Sharma Solutions For Class 8 Chapter 6 Algebraic Expressions And Identities Download Free Pdf




Questions On Algebraic Expressions Algebraic Identities Algebraic Formulas
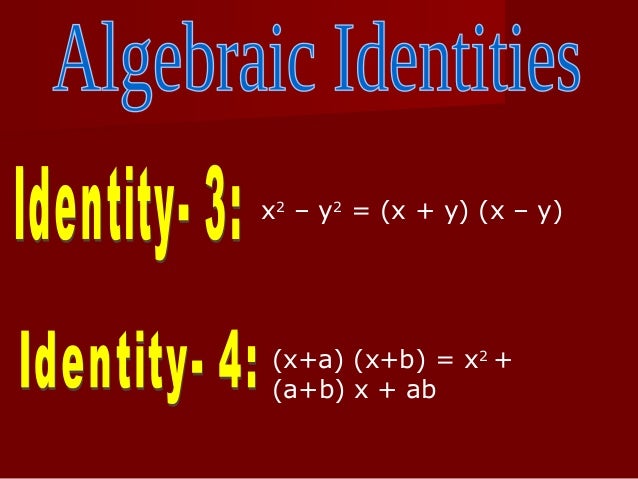
From the identity xm ym= (x y)(xm 1 xm 2y ym 1) it is clear that x i x j divides all entries of the new ithcolumn Thus, x i x j divides the determinant This holds for all iActive Oldest Votes 2 If the neutral element is 0 and you want to find the inverse of a ∈ G, that means you want to find B such that 0 = a ∗ b This implies 0 = a ∗ G b = a × Q b Q a Q b = ( a Q 1) × ( b Q 1) − Q 1 1 = ( a Q 1) × Q ( b Q 1)Problem Solve (x 3) (x – 3) using algebraic identities Solution By the algebraic identity, x 2 – y 2 = (x y) (x – y), we can write the given expression as;




Using Identities Prove That X Y Z 2 3 Xy Yz Zx Where X Y Z Are Positive Real Numbers Maths Polynomials Meritnation Com
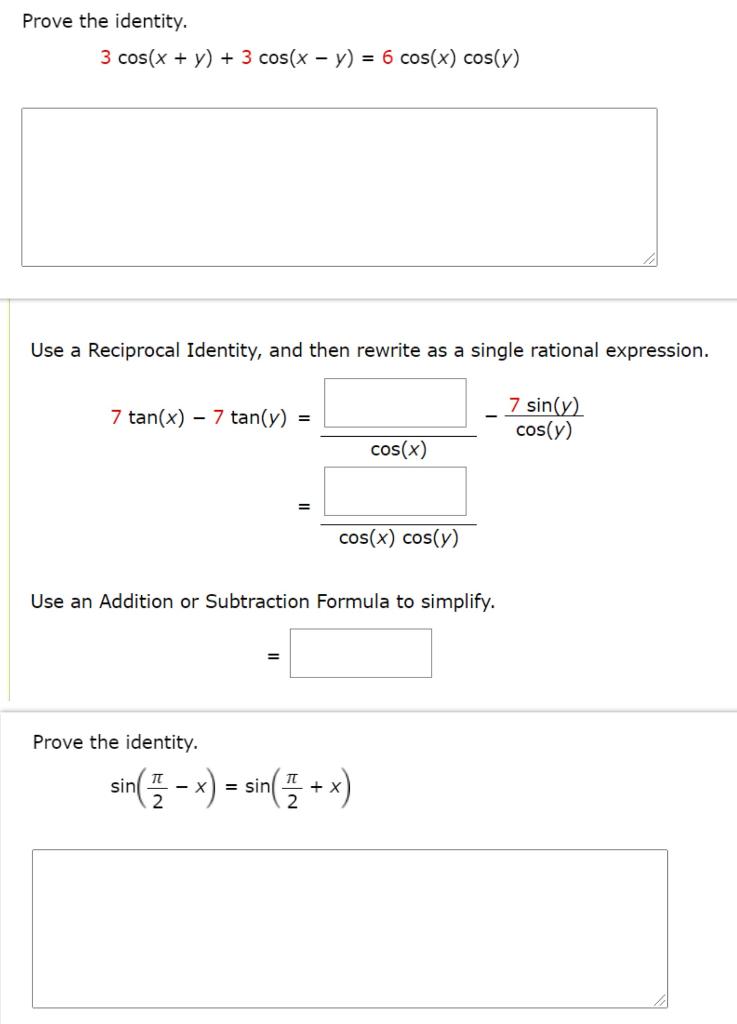



Prove The Identity 3 Cos X Y 3 Cos X Y 6 Chegg Com
Answer In the given problem, we have to simplify the value of each expression (i) Given We shall use the identity for each bracket x 2 2 y 3 2 z 4 2 2 x 2 y 3 2 y 3 z 4 2 x 2 z 4 By arranging the like terms we get Now adding or subtracting like terms, Hence the value of Ex 25, 9Verify (i) x3 y3 = (x y) (x2 – xy y2)LHS x3 y3We know (x y)3 = x3 y3 3xy (x y)So, x3 y3 = (x y)3 – 3xy (x y) = (x y)3 – 3xyMentally examine the expansion of math(xyz)^3/math and realize that each term of the expansion must be of degree three and that because mathxyz/math is cyclic all possible such terms must appear Those types of terms can be represented




Ppt Polynomials Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




Pdf On The Identity Of Fermat S Equation
The identity x / y − y / x = ( y x) ( y − 1 − x − 1) Difference of perfect square asserts that the expression y 2 − x 2 factorizes as ( y x) ( y − x) On the train home last night, I noticed a variant on this Namely, that x / y − y / x factorizes as ( y x) ( y − 1 − x − 1) Explicitly Proposition Let R denote aFor example, the polynomial identity (x 2 y 2) 2 = (x 2 – y 2) 2 (2xy) 2 can be used to generate Pythagorean triples Suggested Learning Targets Understand that polynomial identities include but are not limited to the product of the sum and difference of two terms, the difference of two squares, the sum and difference of two cubes, theCalled an identity element with respect to if e x = x = x e for all x 2A Example 1 1 is an identity element for multiplication on the integers 2 0 is an identity element for addition on the integers 3 If is de ned on Z by x y = x y 1 Then 1 is the identity 4 The operation de ned on Z by x y = 1 xy has no identity element




Given A X 3 Y 3 If A 3i Where I Is The Identity Matrix Of Order 2 Find X And Y Brainly In




If X 3 A N D Y 1 Find The Values Of Each Of The Using Identity X 7 Y 3 X 2 49 Y 2 9 X Y 21
Ax ay =a(x y)?Simplify (X Y)3 − (X − Y)3 Maharashtra State Board SSC (English Medium) 8th Standard Textbook Solutions 3717 Important Solutions 1 Question Bank Solutions 1905 Concept Notes & Videos 226 Concept Factorisation using Identity a3 b3 = (a b)(a2 ab b2)Consider x^ {2}y^ {2}xy22xy as a polynomial over variable x Find one factor of the form x^ {k}m, where x^ {k} divides the monomial with the highest power x^ {2} and m divides the constant factor y^ {2}y2 One such factor is xy1 Factor the polynomial by dividing it by this factor




Class 9 Polynomial 2 Coordinate Geometry Linear Equation In Two Variables Euclid S Geometry Lines And Angles Notes




Algebraic Identities 6 And 7 Youtube
Multiplying by the identity The "identity" matrix is a square matrix with 1 's on the diagonal and zeroes everywhere else Multiplying a matrix by the identity matrix I (that's the capital letter "eye") doesn't change anything, just like multiplying a number by 1 doesn't change anything This property (of leaving things unchanged by multiplication) is why I and 1 are each called theGet stepbystep solutions from expert tutors as fast as 1530 minutes Your first 5 questions are on us!Python Tryit Editor v10 × Change Orientation x = "apple", "banana" y = "apple", "banana" z = x print (x is z) # returns True because z is the same object as x print (x is y) # returns False because x is not the same object as y, even if they have the same content print (x == y) # to demonstrate the difference betweeen "is" and



1



How To Evaluate Using The Identity X Y 3 X3 Y3 3x2y 3xy2 Youtube
Identities involving trig functions are listed below Pythagorean Identities sin 2 θ cos 2 θ = 1 tan 2 θ 1 = sec 2 θ cot 2 θ 1 = csc 2 θ Reciprocal IdentitiesPolynomial Identities When we have a sum (difference) of two or three numbers to power of 2 or 3 and we need to remove the brackets we use polynomial identities (short multiplication formulas) (x y) 2 = x 2 2xy y 2 (x y) 2 = x 2 2xy y 2 Example 1 If x = 10, y = 5a (10 5a) 2 = 10 2 2·10·5a (5a) 2 = 100 100a 25a 2 Solve the identity(xy)^3 Get the answers you need, now!




How To Expand Using The Identity X Y 3 X3 Y3 3x2y 3xy2 Youtube
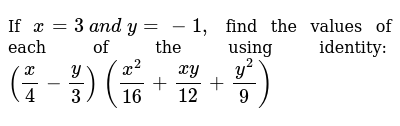



If X 3 A N D Y 1 Find The Values Of Each Of The Using Identity X 4 Y 3 X 2 16 X Y 12 Y 2 9
(x 3) (x – 3) = x 2 – 3 2 = x 2 – 9 Problem Solve (x 5) 3 using algebraic identities Solution We know, (x y) 3 = x 3 y 3 3xy(xy) Therefore, (x 5) 3 = x 3 5 3 3x5(x5)More formally, the number of k element subsets (or k combinations) of an n element set This number can beAccording to an algebraic identity, x 3 y 3 z 3 − 3 x y z = (x y z) (x 2 y 2 z 2 − x y − y z − z x)(1) As x, y & z are positive numbers, (x y z) > 0(2) Now, let's think about another bracket x 2 y 2 z 2 − x y − y z − z x = (1 / 2) ∗ (2 x 2 2 y 2 2 z 2 − 2 x y − 2 y z − 2 z x) = (1 / 2) ∗ (x 2 − 2 x y y 2 y 2 − 2 y z z 2 z 2 − 2 z x x 2) = (1 / 2) ∗ (x − y) 2 (y − z) 2 (z − x




Selina Concise Mathematics Class 8 Icse Solutions Chapter 12 Algebraic Identities Cbse Tuts In 21 Class 8 Mathematics Chapter




Experiment No 2 Boolean Algebra
3 Answers3 One way of looking at this is as a consequence of distributivity, where P Q R ≡ ( P Q) ( P R) Then you'll have This is known as the third distributive law (see, eg, this page ) I think your proof is correct taking LHS XX'Y= (XX') (XY) OR distributes over AND 1 (XY) (XX'=1) XY=RHS 1 is identity for ANDSolution (x 3 8y 3 27z 3 – 18xyz)is of the form Identity VIII where a = x, b = 2y and c = 3z So we have, So we have, (x 3 8y 3 27z 3 – 18xyz) = (x) 3 (2y) 3 (3z) 3 – 3(x)(2y)(3z)= (x 2y 3z)(x 2 4y 2 9z 2 – 2xy – 6yz – 3zx)Xy 2 cos x y 2 sinx siny= 2sin x y 2 cos xy 2 cosx cosy= 2cos xy 2 cos x y 2 cosx cosy= 2sin xy 2 sin x y 2 The Law of Sines sinA a = sinB b = sinC c Suppose you are given two sides, a;band the angle Aopposite the side A The height of the triangle is h= bsinA Then 1If a



Factorize X X 3 Y 3 3xy X Y Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




Class 9 Polynomial 2 Coordinate Geometry Linear Equation In Two Variables Euclid S Geometry Lines And Angles Notes
In a way we can say that factorise is the reverse of expand and that's exactly what we are doing in this videoThis video shows how to factorise using the id1) associative 2) commutative 3) distributive 4) identity 2 The statement =2 is an example of the use of which property of real numbers?Practice with the properties of real numbers The word NUMBERS implies the answer will deal only with numbers The word X implies the answer will contain a variable, but not necessarily the variable x A B Distributive Property (Numbers) 3 (5 2) = 15 6 Commutative Property of Addition (Numbers) 3 7 = 7 3




Ppt Polynomials Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




Find The Following Squares By Using The Identities I B 7
Since x − y = 3 xy=3 x − y = 3 implies y = x − 3, y=x3, y = x − 3, substituting this into the given identity gives a x (x − 3) b x c (x − 3) 9 = 0 a x 2 (− 3 a b c) x − 3 (c − 3) = 0 \begin{aligned} ax(x3)bxc(x3)9&=0\\ ax^2(3abc)x3(c3)&=0 \end{aligned} a x (x − 3) b x c (x − 3) 9 a x 2 (− 3 a b c) x − 3 (c − 3) = 0 = 0Plot of the six trigonometric functions, the unit circle, and a line for the angle = radians The points labelled 1, Sec(θ), Csc(θ) represent the length of the line segment from the origin to that point Sin(θ), Tan(θ), and 1 are the heights to the line starting from the axis, while Cos(θ), 1, and Cot(θ) are lengths along the axis starting from the originIf x x x and y y y are real numbers such that x y = 7 xy=7 x y = 7 and x 3 y 3 = 133 x^3y^3=133 x 3 y 3 = 1 3 3, find the value of x y xy x y Submit your answer 3 3 ( 1640 ) 1 3 \sqrt{\sqrt{\sqrt3{\color{#3D99F6}{}} {\sqrt3{\color{#3D99F6}{} \color{teal}{3(1640) 1}}}}} 3 6 4 0 0 0 3 6 4 0 0 0 3 ( 1 6 4 0 ) 1




Factorize 8 X Y 3 27 X Y 3 Youtube




How To Verify Algebric Identity X Y 3 X3 3xy X Y Y3 Maths Polynomials Meritnation Com
(iii) (998) 3 = () 3 =1000 3 – 2 3 – 3x 1000x 2() Using identity (xy) 3 =x 3y 33xy (xy) =() = 8 – = Question 8 Factorise each of the following




Learn Algebraic Identity Of X Y And X Y In 3 Minutes




Ex 9 5 3 Find The Squares By Using Identities I B 7 2




Learn Algebraic Identity Of X Y And X Y In 3 Minutes




Class 9 Polynomial 2 Coordinate Geometry Linear Equation In Two Variables Euclid S Geometry Lines And Angles Notes




Ex 9 4 3 V Simplify X Y 2x Y X 2y X Y Class 8




What Is An Identity Shashank Tutorial




X 3 Y 3 117 8 X Y 3 2 X 2 Xy Y 2




Ex 2 5 12 Verify That X3 Y3 Z3 3xyz 1 2 Ex 2 5



Prove The Identity Sin X Y Sin X Y 2 Cos X Chegg Com



Expand 1 X Y 3 Whole Cube Studyrankersonline




2 Solve It Plz Q If X Y 10 And Xy 21 Find The Value Of X3 Y3 Using Identity Maths Polynomials Meritnation Com




V3 Using The Identity X A X B X A B X Ab Find Ou Scholr




Algebraic Identities Of Polynomials A Plus Topper



Arxiv Org Pdf 1007 2285




X Y X Y Which Of The Following Equation Must Be An Identity Z Y Z X Z Y Z X Y Pdf Teaching Mathematics Mathematical Objects




Pdf On Trace Forms On A Class Of Commutative Algebras Satisfying An Identity Of Degree Four




Algebraic Identities Of Polynomials A Plus Topper
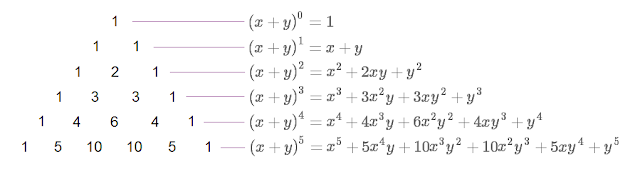



Math Garden Binomial Identity




Using Identity Viii X3 Y3 Z3 3xyz X Y Z X2 Y2 Z2 Xy Yz Zx Solve The Following Question 8x3 Y3 27z3 18xyz Maths Polynomials Meritnation Com



Lines And Am Nles




Ex 9 4 3 Vi Simplify X Y X 2 Xy Y 2 Chapter 9 Class 8




Learn Algebraic Identity Of X Y And X Y In 3 Minutes




Predicate Logic Translation Gregory Chapter 5 3 5




9 Verify I X3 Y3 X Y X2 Xy Y Ii P X Y X2 Xy Scholr




Class 9 Polynomial 2 Coordinate Geometry Linear Equation In Two Variables Euclid S Geometry Lines And Angles Notes




X Y 3 Y Z 3 Z X 3 3 X Y Y Z Z X 2 X3 Y3 Z3 3xyz Mathematics Topperlearning Com T86qex55




Ppt Polynomials Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



1




Ex 2 5 9 Verify I X 3 Y 3 X Y X 2 Xy Y 2 Teachoo




Learn Algebraic Identity Of X Y And X Y In 3 Minutes




Ncert Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Exercise 2 5 Polynomials




Class 9 Polynomial 2 Coordinate Geometry Linear Equation In Two Variables Euclid S Geometry Lines And Angles Notes




Algebraic Identities Of Polynomials A Plus Topper



Lines And Am Nles




What Are The Factors Of X Y 3 X3 Y3 Brainly In



Www Topperlearning Com Answer Using Identities Prove That X Y Z 2 3 Xy Yz Zx Where X Y Z Are Positive Real Numbers 3gc3fduu




Learn Algebraic Identity Of X Y And X Y In 3 Minutes



How To Factorise Using The Identity X Y 3 X3 Y3 3x2y 3xy2 Youtube




Learn Algebraic Identity Of X Y And X Y In 3 Minutes




Pdf Antiflexible Rings With Identity X Y X 0 M Hema Prasad Academia Edu




Ex 9 4 3 V Simplify X Y 2x Y X 2y X Y Class 8




Answered Prove The Polynomial Identity For The Bartleby




A What Is The 2 Times 2 Identity Matrix I B Find Chegg Com



2




Learn Algebraic Identity Of X Y And X Y In 3 Minutes




How To Expand Using The Identity X Y 3 X3 Y3 3x2y 3xy2 Youtube




Selina Concise Mathematics Class 8 Icse Solutions Chapter 12 Algebraic Identities Cbse Tuts



Identity Vs Equation Acute Angel




Cbse Class 9 Maths Lab Manual Algebraic Identity A B 3 A3 3a2b 3ab2 Cbse Sample Papers




Factorise 27 X Y 3 8 X Y 3 Maths Polynomials Meritnation Com




Prove X Y 3 Y Z 3 Z X 3 3 X Y Y Z Z X Brainly In




Entering Identities And The Problem Type Download Scientific Diagram




Learn Algebraic Identity Of X Y And X Y In 3 Minutes




Questions 1 Demonstrate By Means Of Truth Tables Chegg Com




Predicate Logic Translation Gregory Chapter 5 3 5



2




Learn Algebraic Identity Of X Y And X Y In 3 Minutes



Identity Mathematics Wikipedia
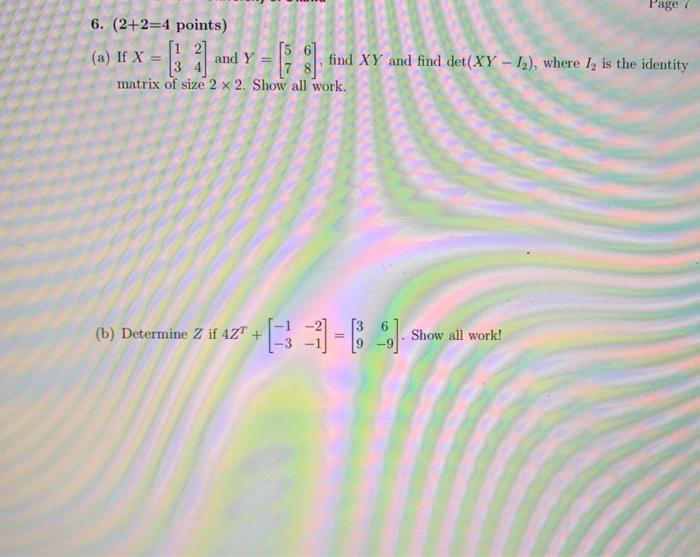



Page 6 2 2 4 Points 1 27 56 A If X And Y 3 Chegg Com




Cos X Y Formula Proof Iventania




Verify X Y 3 X3 Y3 3xy X Y Brainly In



Find The Following Squares By Using Identities I B 7 2 Ii Xy 3z 2 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




Learn Algebraic Identity Of X Y And X Y In 3 Minutes




5 Questions On Advanced Calculus Ii Exam 3 Math 411 Docsity




Art Of Problem Solving




2 Verify Each Of The Following Identities X3 Y3 X Y X2 X Scholr




Learn Algebraic Identity Of X Y And X Y In 3 Minutes
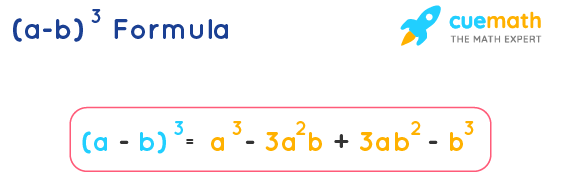



A Minus B Whole Cube Formula Examples A B 3 Formula




Learn Algebraic Identities Of X Y And X Y In 3 Minutes



Pub Ist Ac At Mbilu Quiz 2 solution Pdf




Prove The Identity Simplify At Each Step 3 Cos X Chegg Com




Learn Algebraic Identity Of X Y And X Y In 3 Minutes




Companion Website Example Of Information Displayed If The Identity Download Scientific Diagram




Proof Of Beal S Conjecture




Rd Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 4 Algebraic Identities




If X 3 A N D Y 1 Find The Values Of Each Of The Using Identity X 4 Y 3 X 2 16 X Y 12 Y 2 9




X Y 3 X3 Y3 3xy X Y Brainly In




Derive An Identity For X Y 3 Brainly In



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿